# Future和CompletableFuture
JDK1.5提供的Future可以实现异步计算,这在处理长时间异步调用和并发时非常有用。Future的适用场景有,密集型计算,后台下载文件,爬虫。CompletableFuture则更完善了Future异步特性。
# Future
Future对于具体的Runnable或者Callable任务执行可查询时候完成,获取结果或者取消等操作。
Java 7.0的Future类图结构如下:
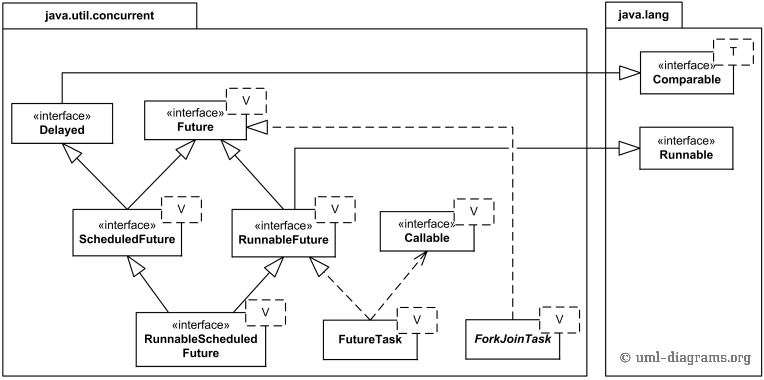
注意:
- Future<V>接口代表了异步计算的结果,V是Future方法返回结果的类型,这个接口的方法允许它等待计算完成,或者取消执行,或者去检查计算是完成了还是被取消了,如果是完成了可以取回计算结果。
- Delayed接口,用来标记应该延迟运行的对象,ScheduledFuture<V>继承自Future<V>和Delayed接口,它通常是ScheduledExecutorService计划任务的结果。
- FutureTask类实现了RunnableFeature接口,这个接口实现了Future和Runnable,它可被一个Executor执行。
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<Integer> future = executor.submit(()->{
Thread.sleep(2000);
return 10;
});
while(!future.isDone()) {
System.out.println("计算中。。。");
Thread.sleep(100);
}
Integer resultInteger = future.get();
System.out.println(resultInteger);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# FutureTask
FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture,而RunnableFuture继承自Runnable和Future的接口,它既可以作为Runnable线程被执行,又可以作为Future得到Callable的返回值,它的两个构造函数分别传入Runnable或Callable。
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
class myTask implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Thread.sleep(2000);
return 10;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
myTask mytask1 = new myTask();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(mytask1);
executor.submit(futureTask);
executor.shutdown();
while(!futureTask.isDone()) {
System.out.println("计算中。。。");
Thread.sleep(100);
}
Integer resultInteger = futureTask.get();
System.out.println(resultInteger);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# ForkJoinPool
JDK1.7之后,为了利用多核CPU的性能优势,可将一个复杂的业务进行拆分,交由多个CPU并行计算,来提高程序的执行性能。它可被看作是一个特殊的Executor执行器,是ExecutorService的补充,特别适合分而治之,递归计算的算法。它包含两个基本操作:
- 分解(Fork):将一个大型业务拆分为若干个小任务在框架中执行。
- 合并(Join):主任务将等待多个子任务执行完毕后进行结果合并。
在ForkJoinPool中需通过ForkJoinTask定义执行任务,ForkJoinTask有两个子类:RecursiveTask(有返回值任务),RecursiveAction(无返回值任务)。结构如下:
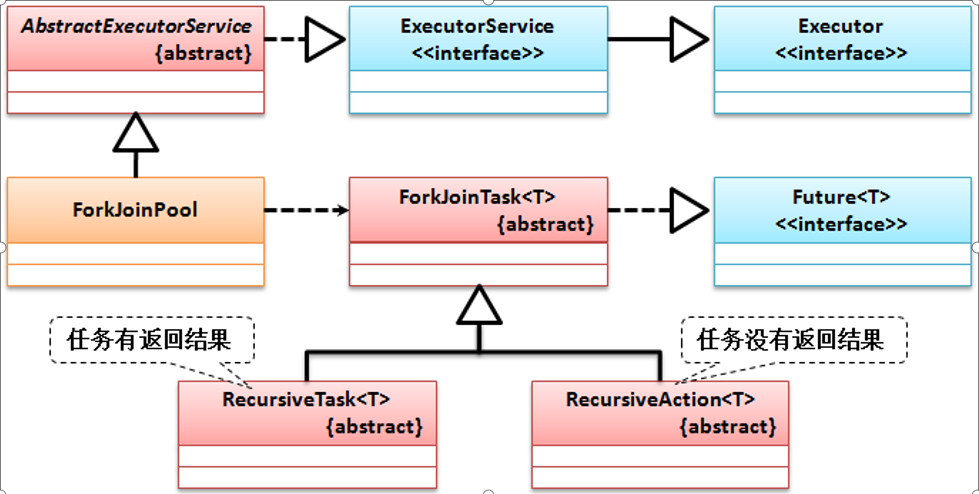
# 有返回值
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
class SumOper extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{
private int startNum;
private int endNum;
public SumOper(int start,int end) {
this.startNum=start;
this.endNum=end;
}
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int sum=0;
if(this.endNum-this.startNum < 10) {
for(int i=this.startNum;i<=this.endNum;i++) {
sum+=i;
}
}else {
int middle=(this.startNum+this.endNum)/2;
SumOper leftAddOper = new SumOper(startNum, middle);
SumOper rightAddOper = new SumOper(middle+1, endNum);
leftAddOper.fork();
rightAddOper.fork();
sum=leftAddOper.join()+rightAddOper.join();
}
return sum;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
SumOper sumOper = new SumOper(0, 100);
ForkJoinPool myPool = new ForkJoinPool();
Future<Integer> future = myPool.submit(sumOper);
System.out.println(future.get());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# 无返回值
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveAction;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class SaveSumResult{
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private int totalNum=0;
public void addNum(int i) {
lock.lock();
totalNum += i;
lock.unlock();
}
public int getTotalNum() {
return totalNum;
}
}
class SumOper extends RecursiveAction {
private int startNum;
private int endNum;
private SaveSumResult result;
public SumOper(int start, int end,SaveSumResult obj) {
this.startNum = start;
this.endNum = end;
this.result=obj;
}
@Override
protected void compute() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (this.endNum - this.startNum < 10) {
for (int i = this.startNum; i <= this.endNum; i++) {
//System.out.println("startNum:"+startNum+";endNum:"+endNum);
result.addNum(i);
}
} else {
int middle = (this.startNum + this.endNum) / 2;
SumOper leftAddOper = new SumOper(startNum, middle,result);
SumOper rightAddOper = new SumOper(middle + 1, endNum,result);
super.invokeAll(leftAddOper, rightAddOper);
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
SaveSumResult result = new SaveSumResult();
SumOper sumOper = new SumOper(0, 100,result);
ForkJoinPool myPool = new ForkJoinPool();
myPool.submit(sumOper);
while (!sumOper.isDone()) {
Thread.sleep(100);
}
if (sumOper.isCompletedNormally()) {
System.out.println(result.getTotalNum());
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
# CompletableFuture
虽然Future提供了异步任务执行能力,但是它有一些局限性:
- 对于线程执行结果的获取只能够采用阻塞或轮询的方式进行处理,这与多线程异步处理理念冲突,轮询的方式造成CPU浪费,也无法及时得到结果。
- 多个Future不串联使用,无法把一个的计算任务结果发送给另一个计算任务,而且也不能组合多个Future。
为了解决这些问题,从JDK1.8开始提供了Future的扩展实现类CompletableFuture,可帮助开发者简化异步编程复杂性。它实现了Future和CompletionStage接口,提供了关于创建,链式调用和组合多个Future的方便方法,它的结构如下
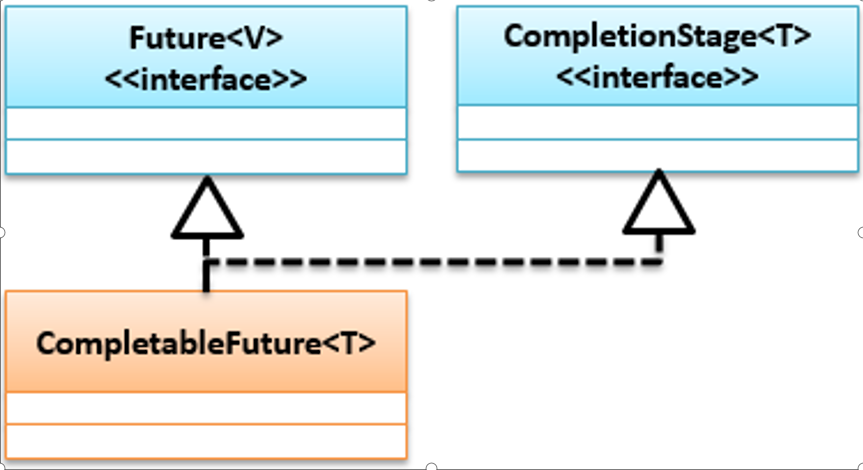
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> completionFuture1 = new CompletableFuture<String>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 手动完成future。
completionFuture1.complete("hello");
}).start();
// 阻塞直到Future完成。
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
System.out.println("子线程完成,获取结果为:"+completionFuture1.get());
System.out.println("子线程完成,获取结果为:"+completionFuture1.get());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 异步运行无返回值方法
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<Void> completionFuture1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("this is void method!");
}
});
CompletableFuture<Void> completionFuture2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("this is void method in lambda!");
});
// 阻塞直到Future完成。
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
completionFuture1.get();
System.out.println("子线程1完成。");
completionFuture2.get();
System.out.println("子线程2完成。");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# 异步运行有返回值方法
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> completionFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<String>() {
@Override
public String get() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello world1!";
}
});
CompletableFuture<String> completionFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello world2!";
});
// 阻塞直到Future完成。
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
System.out.println("子线程1完成。返回:"+completionFuture1.get());
System.out.println("子线程2完成。返回:"+completionFuture2.get());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
通过线程池来执行:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> completionFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "-----hello world!-----1";
},executor);
// 阻塞直到Future完成。
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
System.out.println("子线程1完成。返回:"+completionFuture1.get());
executor.shutdown();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 回调函数
上面我们的主程序在最后输出结果的get()方法处阻塞直到得到结果,如果我们想让主程序一直执行,让子程序执行完执行一个回调函数,可以使用thenApply,thenAccept,thenRun。
# 回调函数返回结果
thenApply()能让回调函数返回一个结果,它需要一个Function<R,T>这样的简单的函数式接口,接受一个T类型参数,得到一个R类型结果。
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> completionFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "-----hello world!-----1";
});
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
CompletableFuture<String> getResult = completionFuture1.thenApply(result->{
System.out.println("已执行完子线程:"+result);
return "得到结果:"+result;
}).thenApply(preResult->{
return "last result:"+preResult;
});
System.out.println("主程序显示结果:"+getResult.get());
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
//System.out.println("子线程1完成。返回:"+completionFuture1.get());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 回调函数不返回结果
如果不想从回调函数中返回结果,只想运行一些代码,可以使用thenAccept和thenRun方法。
thenAccept接收一个Consumer<T>,返回一个CompletableFuture<Void>,该方法能访问CompletableFuture的结果,但却不能再返回其他结果:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> completionFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "-----hello world!-----1";
});
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
CompletableFuture<Void> getResult = completionFuture1.thenAccept(result->{
System.out.println("已执行完子线程:"+result);
});
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
//System.out.println("子线程1完成。返回:"+completionFuture1.get());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
thenRun()接收一个Runnable,返回类型是CompletableFuture<void>。
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> completionFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "-----hello world!-----1";
});
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
CompletableFuture<Void> getResult = completionFuture1.thenRun(()->{
System.out.println("已执行完子线程,这是最后一步!");
});
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
上面的三个回调方法都有两个变体,一个变体是增加一个参数传入线程池,另一个变体是异步执行,上面的thenApply都是同步按顺序执行的,如果用thenApplyAsync,那它是异步执行。
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// ForkJoinPool mypool = new ForkJoinPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> completionFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "-----hello world!-----1";
});
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
CompletableFuture<String> getResult = completionFuture1.thenApplyAsync(result -> {
System.out.println("已执行完子线程:" + result);
return "得到结果:" + result;
}, executor);
System.out.println("主程序显示结果:" + getResult.get());
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
executor.shutdown();
// System.out.println("子线程1完成。返回:"+completionFuture1.get());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 组合两个CompletableFuture
# thenCompose
组合两个有关系的CompletableFuture,现在想先获取一个人的名字,然后根据名字获取他的年龄,获取年龄的CompletableFuture依赖于获取名字的CompletableFuture:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static CompletableFuture<String> GetName() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "li";
});
}
public static CompletableFuture<String> GetNameWithAge(String name) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return name + ":18";
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
CompletableFuture<Object> getResult = GetName().thenApply(name -> GetNameWithAge(name));
CompletableFuture<String> getResult2 = GetName().thenCompose(name -> GetNameWithAge(name));
System.out.println("主程序显示结果:" + getResult.get());
System.out.println("主程序显示结果:" + getResult2.get());
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
注意上面的thenApply是获取Lambda表达式的结果,thenCompose是获取Lambda表达式返回结果的返回值。
# thenCombine
组合两个无关系的CompletableFuture
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetLength() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 100;
});
}
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetWidth() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 200;
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
CompletableFuture<Integer> getResult = GetWidth().thenCombine(GetLength(),(width,length) -> {
System.out.println("width:"+width+";length:"+length);
return width*length;
});
System.out.println("主程序显示结果:" + getResult.get());
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# 组合多个CompletableFuture
全部运行:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetNum1() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(100);
return 100;
});
}
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetNum2() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(200);
return 200;
});
}
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetNum3() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(300);
return 300;
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
CompletableFuture<Void> getResult = CompletableFuture.allOf(GetNum1(),GetNum2(),GetNum3());
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
运行其中一个:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetNum1() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(100);
return 100;
});
}
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetNum2() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(200);
return 200;
});
}
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetNum3() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(300);
return 300;
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
CompletableFuture<Object> getResult = CompletableFuture.anyOf(GetNum1(),GetNum2(),GetNum3());
System.out.println("运行结果:"+getResult.get());
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
注意anyof会返回其中的一个,但是并不是其他的不运行。
# 异常处理
当其中某个回调链出现错误时应该如何解决?需要添加处理异常的方法,使用exceptionally,handle或者whenComplete。
下面是使用exceptionally:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetNum1() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 100/0;
}).exceptionally(e->{
System.out.println("出现错误:"+e.getMessage());
return -1;
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
System.out.println("运行结果:"+GetNum1().get());
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
使用handle:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetNum1() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 100/0;
}).handle((res,e)->{
System.out.println("出现错误:"+e.getMessage());
return res;
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
System.out.println("运行结果:"+GetNum1().get());
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
使用whenComplete:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class Main {
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> GetNum1() {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 100/0;
}).whenComplete((Void,e)->{
System.out.println("出现错误:"+e.getMessage());
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
System.out.println("等待子线程完成!");
System.out.println("主程序休眠中!");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
处理异常时尽量使用上面两种方法,whenComplete捕获异常后会中断。